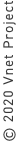Background of the development of VNET Plus:
Exhaustion of IPv4 global addresses:
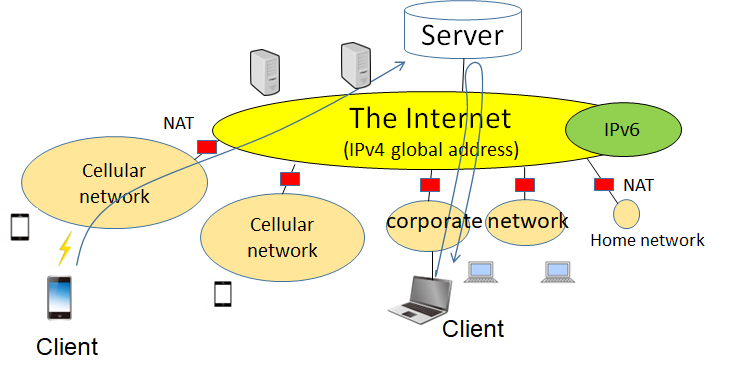
The structure of the present network is shown in the Figure below.
While the Internet is comprised of IPv4 global addresses, most of the communication devices of users are connected to the IPv4 private address areas.
In order to cope with the problem of IPv4 global address exhaustion, private addresses have been introduced as a means of short-term solution.
By defining a part of the IP address space as the private address space, it has become possible for all users to share this space.
With the above-said measures, the problem of global address exhaustion was eased, and we succeeded in extending the life of the Internet at least for the time being.
The Internet and a private network are connected by NAT, that is, a network address translation device.
IPv6 was devised to fundamentally solve the address exhaustion problem of IPv4, but it is taking time to spread.
In this way, the current network contains three types of address areas: IPv4 global, IPv4 private, and IPv6.
Due to these circumstances, there exist the following constraints in TCP/IP communication.
- You cannot start communication from the IPv4 global address area towards the private address areas (due to the existence of NAT traversal problem).
- You cannot make direct communication between a communication device with IPv4 address and another communication device with IPv6 address.
- You cannot continue communication if the network is switched to another network during communication.
- It is difficult to secure P2P communication between end communication devices.
The NAT traversal problem, in particular, is the problem that imposes the most serious constraint to the present network.
Along with the wide-spreading of IoT communication and mobile communication, the above-mentioned constraints give a negative influence on the method of developing applications and hinder the realization of the most suitable systems.
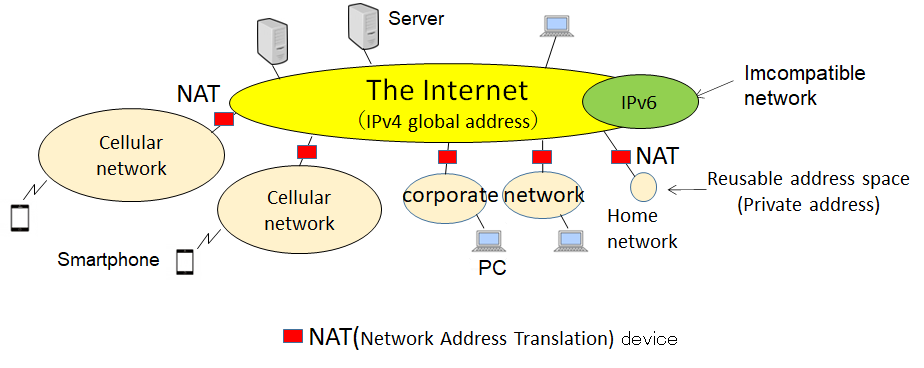
What is the NAT traversal problem?
From the side of the private address networks, multiple servers having unique global addresses can be seen on the Internet, and it is possible for you to designate a specific server with which to communicate.
On the other hand, from the side of the global address network, private address network look as if only one NAT device exists there, and it is not possible to start communication by designating a specific device among multiple communication devices under the NAT.
This issue is called the NAT traversal problem and this situation imposes a big constraint on the IP network.
Thus far, this constraint has not been brought to the surface because it has been hidden behind the policy of enterprise firewalls.
However, with the increasing demand for the opportunity of remote work, the NAT traversal problem has become the largest problem to be solved.
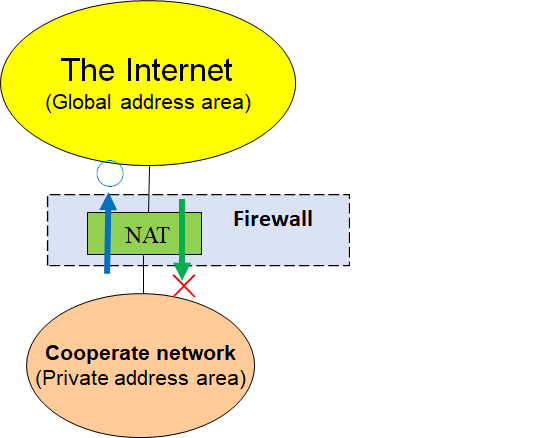
Mobility:
For TCP/IP, it has not been essentially assumed that communication devices would move from their originally set locations.
In TCP/IP, IP addresses are vested with two roles of position identifier and communication identifier.
As shown in the Figure below, if the network in use is switched to another network across the router during communication, the IP address and consequently the communication identifier change and as the result, you cannot continue communication.
In such a situation, the Internet does not do anything to solve the problem owing to the “end-to-end” principle.
From that reason, it is not easy for the Internet to realize the function of making communication possible when the communication device is moving.
(End-to-end principle is a thought (principle) that the function of the Internet is to realize communication at a high speed and in an inexpensive way, and that it should by no means interfere in communication.)
Security (authentication and encryption):
Contents of packets flowing on the Internet can easily be monitored.
Thus, information which you want to be kept confidential needs to be encrypted in order to prevent it from being eavesdropped by third parties.
In addition, there is a necessity to verify whether the communication partner is the real one.
For that reason, it is indispensable to combine the technology for authentication with that for encryption.
Both encrypted communication and personal authentication can be realized when communication technology and encryption technology are combined.
Although such combined technology is partially incorporated in TCP/IP, it is difficult to guarantee solid security between end communication devices directly, from the constraints of TCP/IP as mentioned above.
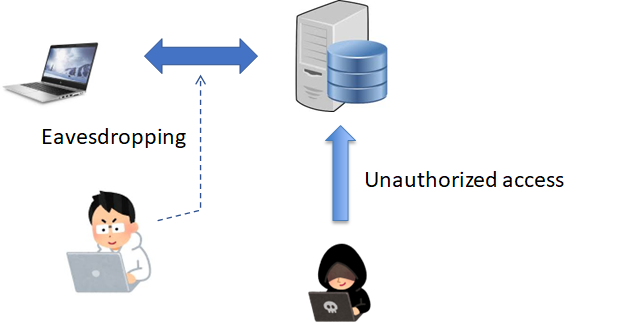
What is client/server system?
We have presently the so-called client/server system (hereafter “CS system”) as a representative technology to command the present-day network.
CS system is composed of a server providing service and multiple clients to receive the service.
In CS system, communication needs to be initiated from the client side all the time.
Furthermore, the server needs to be set on the place where a communication path can be established from the side of the client.
CS system can realize a wide range of services without being bothered by the NAT traversal problem, when the server is set on the Internet.
From the above-said situation, most of the present-day applications are being realized by utilizing CS system.
Even for the case where information is exchanged between clients, communication is conducted by way of conversion to a method of going through a server.
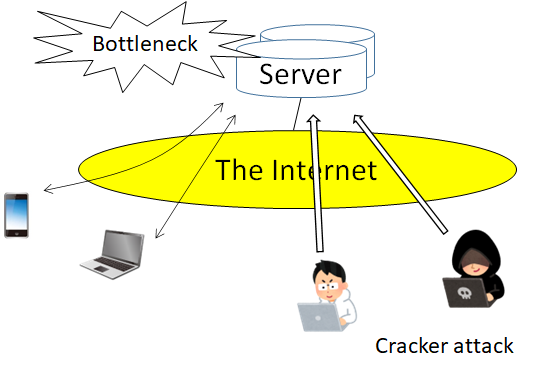
Issues ascribed to the server:
For a CS system, there exist the following issues from the viewpoint of operation and performance.
As regards the operational aspect, the highest level of security needs to be taken into consideration because of the fact that every information goes through the server.
The common practice here is that a public key certificate is issued to each server for the purpose of server authentication and encrypted communication.
However, specialized knowledge is required to obtain the certificate, and fairly high maintenance costs may also be required.
Furthermore, duplication measures are required because the impact could be large once a server failure occurs.
As regards the performance aspect, it is necessary to thoroughly examine the scalability because there are cases where the server itself becomes a bottleneck for processing.
In addition, communication delays between end devices could disproportionally increase as a result of redundant routes.
Due to the above-mentioned issues, there exists a big hurdle to start providing safe services.
Benefits of using VNET Plus
VNET Plus will take the network back to what it should be and realize n:n free communication.
In addition, we added the function of group communication and complete P2P communication security.
If you apply VNET Plus, you don't have to be aware of the existence of NAT or the difference between IPv4 and IPv6, and you can freely communicate with each other.
It is not necessary to change the definition of the communication group no matter how the communication device moves.
Even if you move while communicating, the communication will continue.
Users only need to install VNET Plus as an application on their communication device and perform simple settings.
Consequently, using VNET Plus has the following benefits.
It makes it possible for you to do remote working with enhanced security and an enlarged communication range while maintaining the existing system as it is.
Using VNET Plus, you will be able to develop new types of applications based on your new ideas assuming a huge secure LAN and apply them to wide-range systems including the Internet.